“Chimneys ensure safe exhaust gas release in industrial processes, focusing on stability, emissions control, and environmental sustainability.”
Chimneys (smoke stacks)
Designed to safely release exhaust gases, smoke, and other byproducts produced during industrial operations into the atmosphere.
INTRODUCTION TO CHIMNEYS
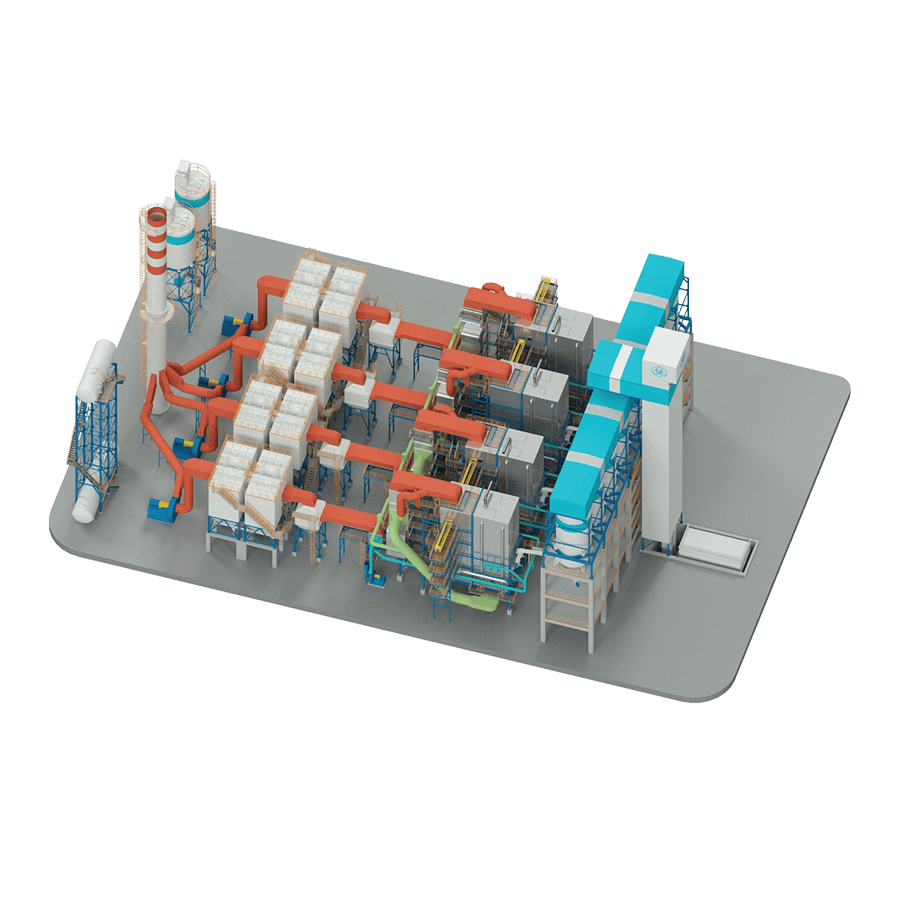
Chimneys, also known as smoke stacks, play a crucial role in various industrial processes. These tall structures are designed to safely release exhaust gases, smoke, and other byproducts produced during industrial operations into the atmosphere. In this article, we will delve into the components, design considerations, types, and environmental impact of industrial chimneys.

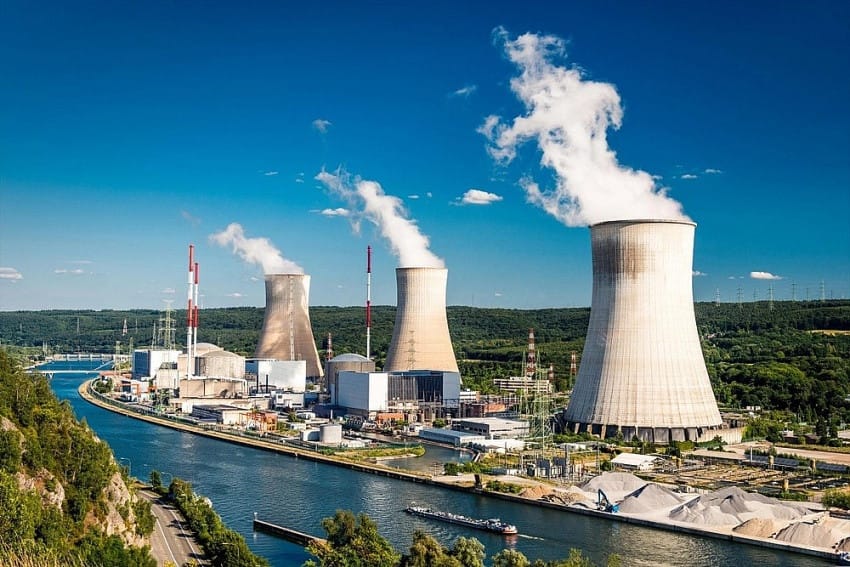
Figure – Industry in dramatic red sunset light. Chimneys and cooling tower of a coal-fired power station.
COMPONENTS OF AN INDUSTRIAL CHIMNEY
- Flue Gas Outlet: This is the uppermost part of the chimney where exhaust gases are discharged into the atmosphere.
- Lining: The chimney’s interior is typically lined with refractory materials to protect the structure from high temperatures and corrosive gases.
- Shell: The outer shell provides structural integrity and protection against environmental factors.
- Base and Foundation: The chimney is anchored to a base or foundation to ensure stability and withstand wind loads.
- Platforms and Ladders: These are installed to facilitate inspection, maintenance, and repair activities.
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
- Height: The height of an industrial chimney is determined by factors such as plume dispersion requirements, local regulations, and the need to prevent ground-level pollution.
- Diameter: The chimney’s diameter depends on the volume and temperature of the exhaust gases and the desired flow velocity.
- Material: Chimneys are typically constructed using materials like concrete, steel, or brick, chosen based on cost, durability, and chemical resistance.
- Structural Stability: Chimneys must be designed to withstand wind loads, seismic forces, and other external factors to ensure their stability.
- Heat Dissipation: Chimneys should have adequate insulation and cooling mechanisms to prevent excessive heat transfer to surrounding structures.
TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL CHIMNEYS
- Single-Flue Chimney: This is the most common type, consisting of a single flue or exhaust channel.
- Multi-Flue Chimney: These chimneys feature multiple flues, allowing the release of emissions from different sources or units.
- Self-Supported Chimney: These tall, slender chimneys are capable of standing without external support due to their structural design.
- Guyed Chimney: Guy wires or cables support these chimney(s), especially in areas prone to high winds or seismic activity.
- Steel Stack: Steel chimneys offer advantages such as ease of construction, versatility, and corrosion resistance.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT AND REGULATION
- Air Pollution: The release of pollutants from industrial chimney(s) can contribute to air pollution, leading to adverse effects on human health and the environment. Stringent emission regulations are in place to control and minimize these emissions.
- Monitoring and Control: Continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) are often installed to measure the quantity and composition of pollutants being released. This data helps industries comply with regulations and implement control measures.
- Renewable Energy: The increasing shift towards renewable energy sources like wind and solar power reduces the reliance on chimneys for fossil fuel combustion, thus mitigating their environmental impact.
- Sustainability: The design and operation of industrial chimneys are evolving to incorporate sustainable practices, including the use of cleaner fuels, improved emission control technologies, and energy-efficient processes.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, industrial chimney(s) are essential components of many industrial processes. Various factors such as emissions control, structural stability, and regulatory compliance influence their design, construction, and operation. As industries continue to prioritize environmental sustainability, the role of industrial chimneys is evolving to minimize their impact on air quality and human health.
(Vn-Industry.)
Home page: https://vn-industry.com/